There once was a time when it was just assumed that by the early 21st century humans would be well on the way in space exploration. Of course, a trip to the moon was always considered the first stop – or ‘start’.
On 20 July 1969, Americans were glued to their television sets as they watched images of Apollo 11 touch down on the Moon’s Sea of Tranquility – the words, The Eagle has landed, went into the history books. Four more manned space flights to the Earth’s only natural satellite would occur between 1969 and 1972 but none were as exciting or interesting to the public as the first.
When people of the Earth saw the barren landscape – and no little green men to welcome the Earthlings – they lost interest in the thought of man on the moon. In the decades that followed there was more interest in conspiracy literature regarding the moon landing as a fraud – with many people believing that it never happened at all. The bulk of this argument focuses on the first expedition to the Moon, and rarely if ever, do the following four missions appear in that regard. The bottom line of the entire Moon missions experience is that nothing much came out of it, except a huge cottage industry of books, films, videos, and conventions all designed around a kind of myth-making.
Needless to say, it’s now the 21st century and humans are no closer to galactic space exploration than they were in 1969. Yes, there are companies working really hard at making this a reality – some day. Still, with this in the works, very few possess the wonder of space exploration that the world did before and during the original Space Age. Perhaps it’s because the entire science fiction genre has turned out so many dark, violent, and foreboding works that there is less wonder and more fear of what is ‘out there’. Or, perhaps the world has become so consumed with the terrors of this world that when it comes to other worlds, ‘we ain’t got time for that.’
Be that as it may, let’s focus just a bit on the wonder and the magic that once was.
Werner Büdeler was one of the earliest writer/journalists in the space-pop tradition. His works helped spread an interest in, and an understanding of, modern scientific principles in everything from the atom, to astronomy, to aerospace – the last two were his specialty.
From among his earliest works one book stands out for its classic imaginative qualities – Flug zum Mond (Flight to the Moon), 1960. Originally published in 1954 with the title, Junge, das ist Tempo (Boy, that’s Speed), it’s a gem for the illustrations alone.

Artist Erik Theodor Lössig took the basic conceptual ideas of engineers like Wernher von Braun, H. E. Ross, and R. A. Smith, and created some wonderful works in black and white. They capture the visionary ideas of the early Space Age perfectly.
The idea of getting to the moon involved first building an outer space station which would then be used to build the modules that would launch to the moon – the idea being that launching from space itself decreased the amount of energy which would otherwise be used just to get out of the Earth’s atmosphere and gravitational pull. This allowed for the conservation of fuel that would be needed for the trek to the moon – and someday beyond.
As you can see from these concepts, the journey to the Moon wasn’t thought to be a step-on-step-off experiment – these imagineers saw the Moon as a new frontier for settlement as a base, and potentially a launching site for further space exploration.

A two-stage large-scale rocket designed to transport materials.

A Multi-stage Rocket designed to transport technicians and construction workers.

Separation of the personnel transport top stage.

The Space Pilot

The Central Station – weightless in zero gravity

The Space Station Construction Site

Mounting the Mirror – The mirror would utilize solar energy and act as a reflective shield, the ‘Space Taxi’ would transport materials and technicians.

The outer station revolves around the Earth.
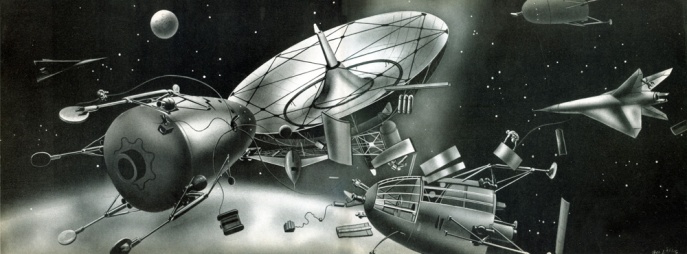
Assembly of the Lunar ships.

Moon Landing

The First Step

The Moon Base
As we now know, this wasn’t the way things were done with the Apollo program – the US was in too much of a rush to beat the USSR in the ‘space race’ to take the time for such an intelligent endeavor. Perhaps, someday, these still viable ideas will be considered when human space exploration once again captures the world’s imagination.
A special thanks to Retro-Futurismus for the beautiful scans – they are much better than the images that my well-used copy could have produced.














